Scope 3 Reporting Requirements
An Overview of New Reporting Requirements for Public Financial Companies
PCAF Standards Data OptionsThe Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials’ Global GHG Accounting & Reporting Standard (the “PCAF Standard”) provides one methodology that complements the GHG Protocol and assists financial institutions in calculating their financed emissions. The PCAF Standard was developed for financial institutions to work with the calculation of Scope 3 emissions for the “investment” category of downstream emissions and was endorsed by the drafters of the GHG Protocol.Given the required nature of this reporting, financial firms will need to do the best they can in quantifying these emissions to protect against any claims of lax commitment to corporate social responsibility objectives. The PCAF standards are not particularly specific and in many instances are aspirational, so adopting this standard as a reporting methodology is relatively straight-forward. However, PCAF standards also states that “financial institutions shall use the highest quality data available for each asset class and improve the quality of the data over time.” The challenge using the PCAF standards is to achieve the greatest level of accuracy without imposing an “undue burden.” The PCAF standards are international so they attempt to rank lowest quality to highest quality data inputs with rather generic descriptions. This graphic from the 2019 PCAF North America Report suggests various quality levels. 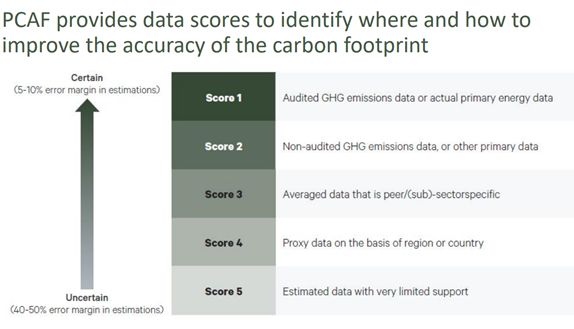
US financial institutions will be evaluated on their emissions reporting based on available US data sources. At the top, the most accurate level would be for each mortgagor or CRE customer to report its emissions to the financial institution. This is obviously not realistic for US financial institution customers so the next best and most accurate option is to obtain actual energy use information for commercial customers where available or to estimate energy use information for residential and CRE customers based on statistical averages for geographic areas. Applying estimates with information on customer segment characteristics such as income and floor space will increase the accuracy of these estimates. For those looking to use publicly available data sources of estimated average energy use information for residential and commercial buildings energy use, there is no public source that provides information below the regional or sometimes state level, which as we document in the See the Notes and Whitepapers Section is critical for accurate carbon emissions reporting illustrating the advantage of MAISY ZIP-level energy use-based emissions data compared to state or regional averages. MAISY Scope 3 Emissions Data for Financial FirmsMAISY Scope 3 Databases are the most accurate available source of mortgage and commercial real estate loan financed emissions. Databases provide average electricity kWh, natural gas and fuel oil use for residential and commercial buildings in individual ZIP codes across the US. Segment averages based on residential income and floor space and commercial business type and floor space are recommended to enhance accuracy.For commercial real estate loan emissions, in addition to ZIP code business/floor space averages energy use information has been curated from CRE owners for more than 15,000 larger commercial properties in various US locations. MAISY Scope 3 Emissions Data for Financial Firms are developed from MAISY ZIP-level Utility Customer Energy Use Databases. MAISY Databases were introduced in 1995 and are updated on an annual basis. These data have been applied by some of the largest utilities, equipment manufacturers, state regulatory agencies, the US Department of Energy for appliance efficiency standards, and other energy related organizations to assess the same kind of utility customer data targeted by the new SCE proposed rules. |
